The global economy experienced unprecedented shifts following the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic. These changes rippled through financial markets, significantly impacting currency exchange rates. One of the most closely watched pairings is the euro to dollar exchange rate. Understanding its dynamics is crucial for businesses, investors, and individuals alike, especially when considering everyday transactions or larger financial decisions involving euro to usd conversions, such as understanding how much 19 Euro In Usd is worth today.
This article delves into how the Covid-19 pandemic altered the dynamics of the euro to dollar exchange rate. By examining research that utilizes advanced analytical techniques, we aim to provide a clearer picture of the factors influencing this critical exchange rate during times of global crisis and what it means for currency values.
Analyzing the Shifting Landscape of Exchange Rates During Crisis
Economic crises often trigger significant movements in exchange rates. The Covid-19 pandemic, with its widespread lockdowns and economic disruptions, presented a unique scenario to observe these shifts. Researchers have investigated how this global event has redefined the determinants of the euro to dollar exchange rate, moving beyond typical market factors.
Early studies on previous financial crises, like the 2007-2009 global financial crisis, showed that major currencies like the US dollar and the euro often appreciated against other currencies. This phenomenon was partly attributed to a “safe-haven” effect, where investors sought stability in these currencies during turbulent times. However, the Covid-19 pandemic introduced new layers of complexity, impacting not only investor sentiment but also fundamental economic activities on a global scale.
To understand these complexities, a study utilized spectral non-causality tests to pinpoint the factors driving the euro to dollar exchange rate both before and during the pandemic. This analysis considered a range of variables, including:
- Exchange rate movements of other major currencies
- The performance of the S&P 500 stock market index
- Prices of commodities like oil and gold
- The realized volatility of these financial instruments
This approach allowed for a comprehensive examination of how different market elements interacted and influenced the euro to dollar exchange rate during the pre-Covid and Covid-19 periods.
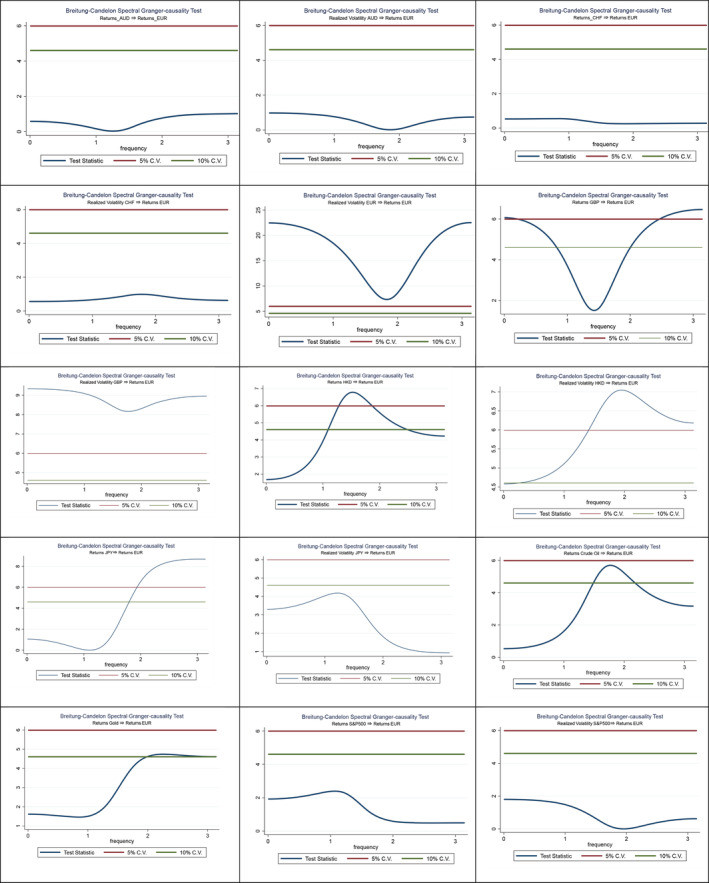 Spectral non-causality tests, pre-Covid-19 era, showing the influence of various financial instruments on the euro to dollar exchange rate.
Spectral non-causality tests, pre-Covid-19 era, showing the influence of various financial instruments on the euro to dollar exchange rate.
The findings revealed a significant shift in the determinants of the euro to dollar exchange rate due to the pandemic. The relationships that held true before Covid-19 were altered as new economic realities took hold.
Markov-Switching Models: Unveiling Volatility Shifts
To further investigate the changes in the euro to dollar exchange rate’s behavior, researchers employed a Markov-Switching (MS) model. This model is designed to identify shifts between different “regimes” or states in time series data. In the context of exchange rates, these regimes often correspond to periods of high and low volatility.
By applying a two-regime MS model, the study aimed to quantify how the Covid-19 pandemic impacted the volatility dynamics of the euro to dollar exchange rate. This involved analyzing the duration and characteristics of high and low volatility states in both the pre-pandemic and pandemic eras.
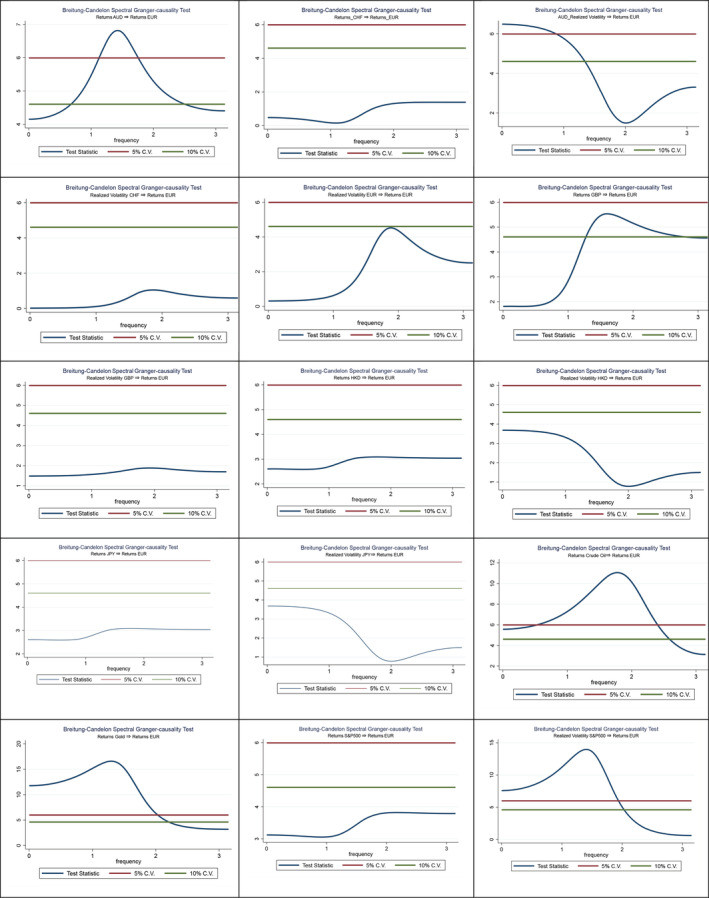 Spectral non-causality tests, actual Covid-19 era, illustrating the changed dynamics of factors affecting the euro to dollar exchange rate during the pandemic.
Spectral non-causality tests, actual Covid-19 era, illustrating the changed dynamics of factors affecting the euro to dollar exchange rate during the pandemic.
The results from the MS model provided striking insights:
- Increased Duration of High Volatility: The study found that the duration of high volatility states for the euro to dollar exchange rate doubled during the Covid-19 era. Before the pandemic, a high volatility state might last approximately 3 days. During the pandemic, this extended to around 6 days. This longer duration of high volatility underscores the heightened uncertainty and instability in the currency markets.
- Higher Volatility Range: Not only did high volatility periods last longer, but the range of volatility within these states was also significantly higher during the pandemic compared to the pre-pandemic period. This means that the fluctuations in the euro to dollar exchange rate were more extreme and unpredictable.
These findings highlight the profound impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on the stability of the euro to dollar exchange rate. The increased and prolonged periods of high volatility have significant implications for anyone dealing with currency exchange, from international businesses managing cash flows to tourists budgeting for a trip and needing to convert 19 euro in usd for their expenses.
Key Determinants of Euro to Dollar Rate: Pre- vs. Post-Pandemic
The spectral non-causality tests revealed which factors significantly influenced the euro to dollar exchange rate in the two distinct periods.
Pre-Covid-19 Era:
Before the pandemic, the euro exchange rate was significantly influenced by:
- Realized volatility of EUR, GBP, and HKD: The inherent volatility within the euro, British pound, and Hong Kong dollar exchange rates themselves were key drivers.
- Returns of HKD, JPY, GBP, Crude Oil, and Gold: Movement in these financial instruments also played a role. Notably, the returns of the British pound and the euro exchange rate showed a strong interdependency, likely due to their close economic ties and geographical proximity.
Covid-19 Era:
The landscape shifted dramatically during the pandemic. The key determinants became:
- Realized volatility of AUD and S&P 500: The volatility of the Australian dollar and the S&P 500 stock market index emerged as significant causal factors. This suggests a broader global market influence, with the US stock market’s volatility becoming a critical factor for the euro-dollar pair.
- Returns of GBP, Crude Oil, and Gold: While the British pound remained influential, commodities like crude oil and gold took on a more prominent role. The increased importance of gold, a traditional safe-haven asset, reflects investor flight to safety during the crisis. The influence of crude oil could be tied to the pandemic’s impact on global demand and supply chains.
This comparison underscores the structural changes in the determinants of the euro to dollar exchange rate. The pandemic shifted the focus from primarily currency-specific factors to broader global market volatility and commodity influences. For individuals tracking exchange rates to understand how much is 19 euro in usd, these shifts mean that a wider range of global economic indicators now play a role.
Policy Implications and Risk Management
The increased volatility and altered dynamics of the euro to dollar exchange rate during the Covid-19 pandemic have significant policy implications. The research highlights the need for robust risk management strategies, especially for businesses engaged in international trade and finance.
One crucial policy tool mentioned is the foreign exchange hedge (FOREX hedge). This strategy allows companies to mitigate risks associated with currency fluctuations by transferring these risks to financial institutions. Given the heightened volatility observed, the use of FOREX hedges becomes even more critical for businesses dealing with euro to dollar transactions.
Furthermore, the econometric models used in this research, particularly the Markov-Switching model, offer valuable tools for policymakers. These models can help in:
- Real-time risk assessment: Identifying shifts to high volatility regimes in real-time allows for timely policy responses.
- Understanding exchange rate determinants: Knowing the key factors influencing the exchange rate enables targeted policy interventions to stabilize currency markets.
- Systemic risk reduction: By understanding and managing exchange rate volatility, policymakers can contribute to reducing overall systemic risk in the financial system.
For individuals and businesses, understanding these dynamics is essential for making informed decisions about currency conversions. Whether it’s converting 19 euro in usd for daily expenses or managing larger sums, awareness of the factors driving exchange rate volatility is key to navigating the complexities of the global currency market.
Conclusion: Adapting to a New Exchange Rate Reality
The Covid-19 pandemic has undeniably reshaped the dynamics of the euro to dollar exchange rate. The research presented demonstrates a clear shift in the factors influencing this rate and a significant increase in its volatility. The duration of high volatility periods has lengthened, and the range of fluctuations has widened, creating a more challenging environment for businesses and individuals dealing with currency exchange.
The findings emphasize the need to adapt to this new reality. For policymakers, this means utilizing advanced models to monitor and manage exchange rate risks effectively. For businesses, implementing robust FOREX hedging strategies is crucial to protect against currency volatility. And for individuals, staying informed about the global economic factors influencing exchange rates is essential for making sound financial decisions when converting currencies like euro to usd.
As the world continues to navigate the aftermath of the pandemic and faces new global challenges, understanding the evolving dynamics of key exchange rates like the euro to dollar will remain paramount. Further research, incorporating new data and variables such as vaccination rates and ongoing economic recovery efforts, will continue to refine our understanding of these complex relationships and help us better prepare for future economic uncertainties.
References
Konstantakis KN, Melissaropoulos IG, Daglis T, Michaelides PG. The euro to dollar exchange rate in the Covid‐19 era: Evidence from spectral causality and Markov‐switching estimation. Int J Fin Econ. 2021;1–9. 10.1002/ijfe.2524
Data Availability
Data available on request from the authors. Data sources for further reading: https://www.histdata.com/download-free-forex-data/; https://finance.yahoo.com/; https://github.com/CSSEGISandData/COVID-19
