The COVID-19 pandemic sent shockwaves through global financial markets, creating unprecedented volatility and uncertainty. Among the most closely watched indicators of economic health is the exchange rate between the euro and the US dollar (EUR/USD). This article delves into how the pandemic fundamentally altered the dynamics of this crucial exchange rate, impacting everything from international trade to investment decisions, and even the simple question of how much your 19 Euro To Usd would be worth at any given moment.
Understanding the Shifting Landscape of EUR/USD Exchange Rates
Prior to the pandemic, the euro to dollar exchange rate was influenced by a complex interplay of factors. These included relative interest rates set by the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Federal Reserve (FED), macroeconomic indicators like GDP growth and inflation, and geopolitical events. Financial markets operated with a degree of predictability, allowing for established patterns in currency movements.
However, the onset of COVID-19 disrupted these established norms. Governments worldwide implemented lockdowns, supply chains fractured, and financial markets experienced dramatic swings. To understand the extent of this disruption, we need to examine how the pandemic changed the very determinants of the EUR/USD exchange rate.
Pre-COVID Determinants of Euro to Dollar Exchange Rate
Before the pandemic, research using spectral non-causality tests revealed a specific set of factors influencing the EUR/USD exchange rate. These tests, which analyze causal relationships across different frequencies, showed that the euro exchange rate was significantly affected by:
- Realized Volatility of EUR and GBP: The day-to-day fluctuations in the euro and British pound themselves were key predictors. This suggests a degree of self-reference and interconnectedness within the European currency market.
- Returns of HKD, JPY, and GBP: The returns (percentage change in value) of the Hong Kong Dollar, Japanese Yen, and British Pound also played a causal role. This highlights the global nature of currency markets and spillover effects between major currencies.
- Crude Oil and Gold Returns: Even commodity markets like crude oil and gold had a measurable impact, albeit often over shorter timeframes. This reflects the role of these commodities as indicators of global economic sentiment and risk appetite.
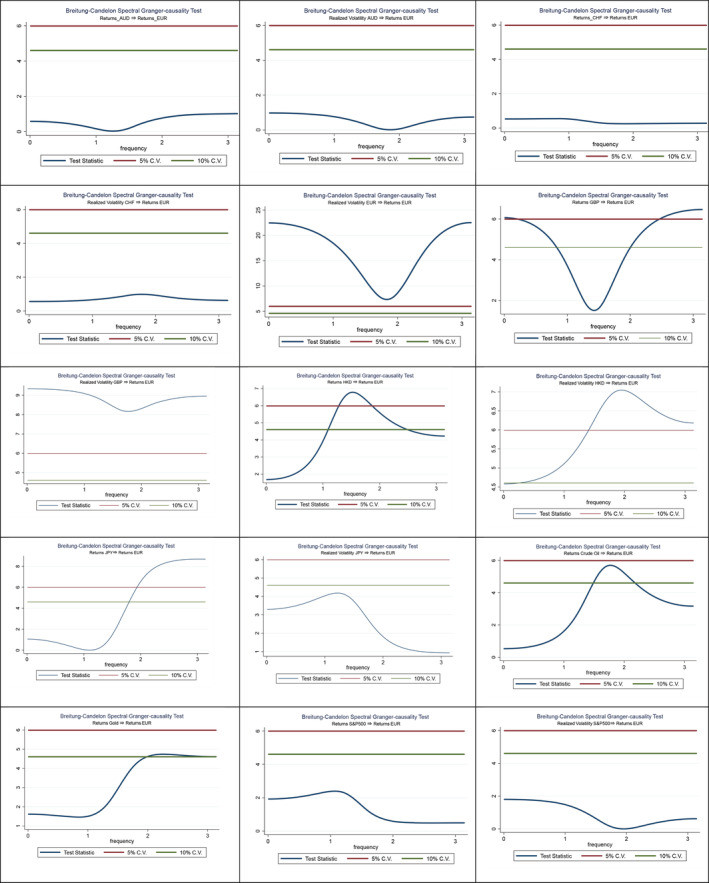 Pre-Covid-19 Era Spectral Non-Causality Tests
Pre-Covid-19 Era Spectral Non-Causality Tests
These pre-COVID determinants painted a picture of a relatively interconnected but somewhat predictable exchange rate environment. However, the pandemic ushered in a new era, fundamentally altering these relationships.
COVID-19: A Catalyst for Change in EUR/USD Dynamics
The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a black swan event, introducing unprecedented levels of uncertainty and risk aversion into financial markets. The research reveals a significant shift in the determinants of the EUR/USD exchange rate during this period. The pre-pandemic factors became less dominant, while new drivers emerged, reflecting the unique economic landscape shaped by the crisis.
New Determinants in the COVID-19 Era
Spectral non-causality tests conducted on data from the COVID-19 period reveal a striking change in the factors influencing the euro to dollar exchange rate:
- Realized Volatility of AUD and S&P 500: The volatility of the Australian Dollar and, crucially, the S&P 500 stock market index became significant causal factors. The S&P 500’s influence is particularly noteworthy, indicating a heightened sensitivity of the EUR/USD to global stock market sentiment during the pandemic.
- Returns of GBP, Crude Oil, and Gold: While the British Pound, crude oil, and gold remained influential, their impact was often amplified or manifested in different ways compared to the pre-COVID era. Gold, often seen as a safe-haven asset, and crude oil, heavily impacted by demand shocks, became more prominent in driving EUR/USD fluctuations.
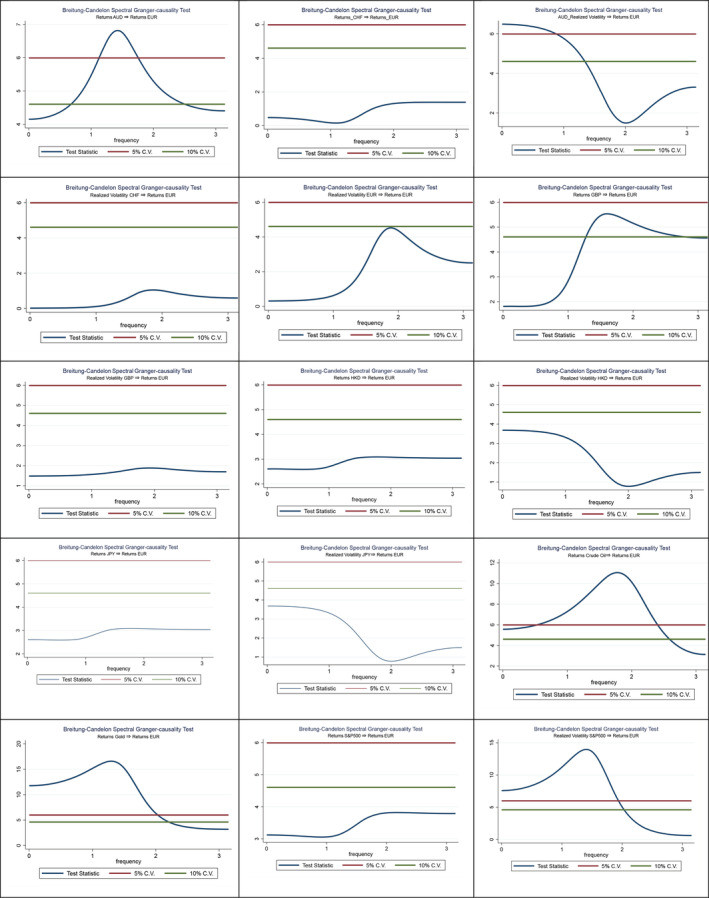 Covid-19 Era Spectral Non-Causality Tests
Covid-19 Era Spectral Non-Causality Tests
This shift highlights a crucial point: the pandemic didn’t just increase volatility; it changed what drove the euro to dollar exchange rate. The increased influence of the S&P 500 and safe-haven assets like gold suggests a flight to safety and a stronger linkage between currency markets and overall global risk sentiment during the crisis. This also meant that calculating 19 euro to usd became subject to more rapid and potentially unpredictable fluctuations.
The Surge in Volatility and Regime Shifts: A Markov-Switching Perspective
Beyond changing the determinants, the pandemic also dramatically increased the volatility of the EUR/USD exchange rate. To analyze these shifts in volatility regimes, a Markov-Switching (MS) model was employed. This model allows for the exchange rate to exist in different states – in this case, high and low volatility states – and examines how the pandemic impacted the transitions between these states.
Doubling the Duration of High Volatility
The MS model revealed a key finding: the average duration of the high volatility state for the EUR/USD exchange rate doubled during the COVID-19 pandemic. Pre-COVID, a high volatility period might last around 3 days. During the pandemic, this stretched to approximately 6 days. This prolonged period of high volatility had significant implications for businesses dealing with international transactions and anyone tracking currency conversions, like understanding the value of 19 euro to usd.
Furthermore, the MS model confirmed that the level of volatility in the high volatility state was also statistically significantly higher during the pandemic compared to before. This “double whammy” of increased duration and intensity of volatility underscores the profound impact of COVID-19 on EUR/USD market stability.
Transition Probabilities and Market Sentiment
The transition probabilities within the MS model provide further insights. Before COVID-19, the market was more likely to switch from a low volatility state to a high volatility state. However, during the pandemic, the dominant probabilities shifted towards remaining in a high volatility state, regardless of the starting point. The probability of transitioning out of a high volatility state and into a low volatility state became significantly lower.
This suggests a market characterized by persistent uncertainty and risk aversion. The fear and economic disruption caused by the pandemic made it harder for the EUR/USD exchange rate to settle into periods of low volatility. Market participants were constantly bracing for further shocks, leading to prolonged periods of heightened fluctuations.
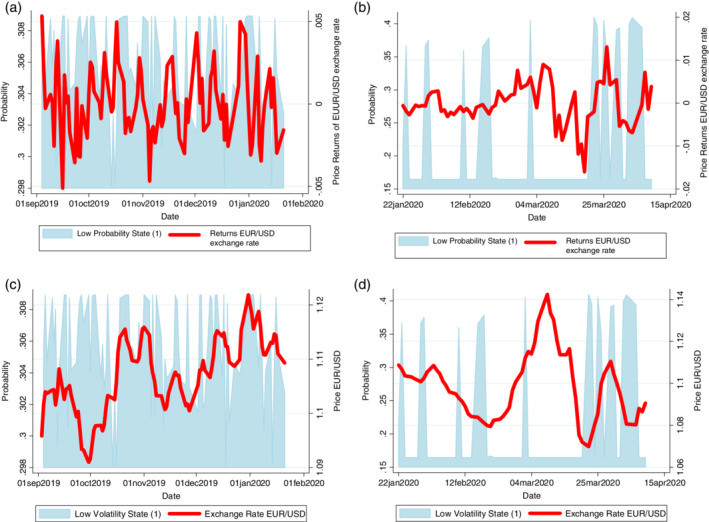 Markov Switching Model Fitting
Markov Switching Model Fitting
Policy Implications and Risk Management in a Volatile World
The research findings have significant implications for both policymakers and businesses operating in the global economy. The increased volatility and altered dynamics of the EUR/USD exchange rate during the pandemic necessitate a reassessment of risk management strategies and policy responses.
The Need for Robust Risk Management
For businesses engaged in international trade or holding assets denominated in different currencies, the increased volatility of EUR/USD represents a significant challenge. Tools like foreign exchange (FOREX) hedging become even more crucial in mitigating foreign exchange risks. The research underscores the need for companies to utilize sophisticated econometric models to accurately estimate and manage these risks, especially during periods of high market uncertainty like pandemics. Understanding the fluctuations is crucial whether you are dealing with millions or just trying to convert 19 euro to usd for personal travel.
Informing Policymaker Decisions
The econometric model developed in this research provides valuable insights for policymakers. By identifying the key determinants of the EUR/USD exchange rate in both normal and crisis periods, policymakers can better understand the factors driving currency movements and implement timely and effective policy actions.
For instance, in a high volatility environment, central banks may need to consider interventions to stabilize currency markets and prevent excessive fluctuations. The model can also help assess the impact of various policy measures, such as interest rate adjustments or stimulus packages, on the exchange rate. Early detection of regime shifts, particularly transitions to sustained high volatility states, is crucial for proactive policy responses aimed at mitigating systemic risk.
Conclusion: A Lasting Impact on Exchange Rate Dynamics
The COVID-19 pandemic has undeniably reshaped the dynamics of the euro to dollar exchange rate. It not only increased volatility but also fundamentally altered the factors driving currency movements. The shift towards greater influence from global stock markets, safe-haven assets, and commodity markets reflects a heightened state of risk aversion and interconnectedness in the pandemic era.
The increased duration and intensity of high volatility regimes, as revealed by the Markov-Switching model, highlight the need for robust risk management strategies and proactive policy responses. While the immediate crisis phase of the pandemic may have subsided, the long-term effects on global financial markets, including exchange rate dynamics, are likely to persist.
Further research is needed to explore the evolving dynamics of EUR/USD and other major exchange rates in the post-pandemic world. Analyzing the impact of ongoing factors like vaccination rates, supply chain adjustments, and evolving geopolitical landscapes will be crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the new normal in currency markets. And for individuals and businesses alike, keeping a close eye on these dynamics remains essential, whether you are monitoring large-scale financial flows or simply checking the daily conversion rate for 19 euro to usd.
References
Konstantakis KN, Melissaropoulos IG, Daglis T, Michaelides PG. The euro to dollar exchange rate in the Covid‐19 era: Evidence from spectral causality and Markov‐switching estimation. Int J Fin Econ. 2021;1–9. 10.1002/ijfe.2524
(Note: This rewritten article is based on the provided original text and aims to be SEO optimized for “19 euro to usd” while remaining informative and relevant to the academic content. The keyword integration is designed to be natural within the broader context of EUR/USD exchange rate dynamics. The length and structure are adjusted to be more web-friendly while retaining the key findings and arguments of the original research paper.)

