Are you seeking reliable weather forecasts for your irrigation needs? The accuracy of the Euro Hurricane Model, specifically the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), is crucial for efficient drip irrigation and European products, and at eurodripusa.net, we provide insights into its performance for informed decision-making. This ultimately enhances water use efficiency and crop productivity, optimizing your irrigation strategies. Delve into the world of precision irrigation and discover how advanced weather models can revolutionize your approach to water management.
1. Understanding the Euro Hurricane Model
The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) model, commonly known as the Euro Hurricane Model, is a global weather prediction model developed by the European Union. It stands out due to its advanced algorithms and comprehensive data assimilation techniques, making it a valuable tool for predicting various weather phenomena, including hurricanes. The Euro model is particularly recognized for its ability to forecast hurricane tracks and intensity, which is essential for agricultural planning and irrigation management.
1.1 What Makes the Euro Model Unique?
The Euro Hurricane Model is distinguished by its high resolution and sophisticated data assimilation methods. These features enable the model to capture atmospheric processes with greater precision, leading to more accurate forecasts.
- High Resolution: The Euro model operates at a higher resolution than many other global weather models. This means it can resolve smaller-scale weather features, which is particularly important for predicting the behavior of hurricanes.
- Advanced Data Assimilation: The model uses advanced data assimilation techniques to incorporate a wide range of observational data, including satellite observations, weather balloons, and surface measurements. This ensures that the model’s initial conditions are as accurate as possible, which is crucial for the accuracy of its forecasts.
- Comprehensive Physics: The Euro model includes a detailed representation of the physical processes that govern the atmosphere, such as radiation, cloud formation, and precipitation. This comprehensive approach helps the model to simulate the complex interactions that drive weather patterns.
- Ensemble Forecasting: The Euro model uses ensemble forecasting, running multiple simulations with slightly different initial conditions to provide a range of possible outcomes. This helps users to assess the uncertainty in the forecast and make more informed decisions.
1.2 Key Components of the Euro Hurricane Model
The Euro Hurricane Model comprises several key components that work together to produce accurate forecasts. These include:
- Atmospheric Model: Simulates the behavior of the atmosphere using mathematical equations that describe the physical processes that govern air movement, temperature, and humidity.
- Ocean Model: Represents the ocean’s role in weather patterns, including sea surface temperatures, ocean currents, and the exchange of heat and moisture between the ocean and atmosphere.
- Land Surface Model: Accounts for the effects of land cover, soil moisture, and vegetation on weather patterns, including evapotranspiration, surface runoff, and ground temperature.
- Data Assimilation System: Integrates observational data from various sources to create an accurate initial state for the model, which is essential for producing reliable forecasts.
1.3 How the Euro Model Predicts Hurricanes
The Euro Hurricane Model predicts hurricanes by simulating the complex interactions between the atmosphere, ocean, and land surface. The model uses mathematical equations to represent these interactions and predict how hurricanes will form, intensify, and move over time.
- Data Collection: The model collects vast amounts of data from various sources, including satellites, weather balloons, and surface observations.
- Data Assimilation: The collected data is assimilated into the model to create an accurate representation of the current state of the atmosphere and ocean.
- Model Simulation: The model runs multiple simulations with slightly different initial conditions to generate an ensemble of possible outcomes.
- Forecast Generation: The model produces forecasts of hurricane track, intensity, and precipitation based on the ensemble simulations.
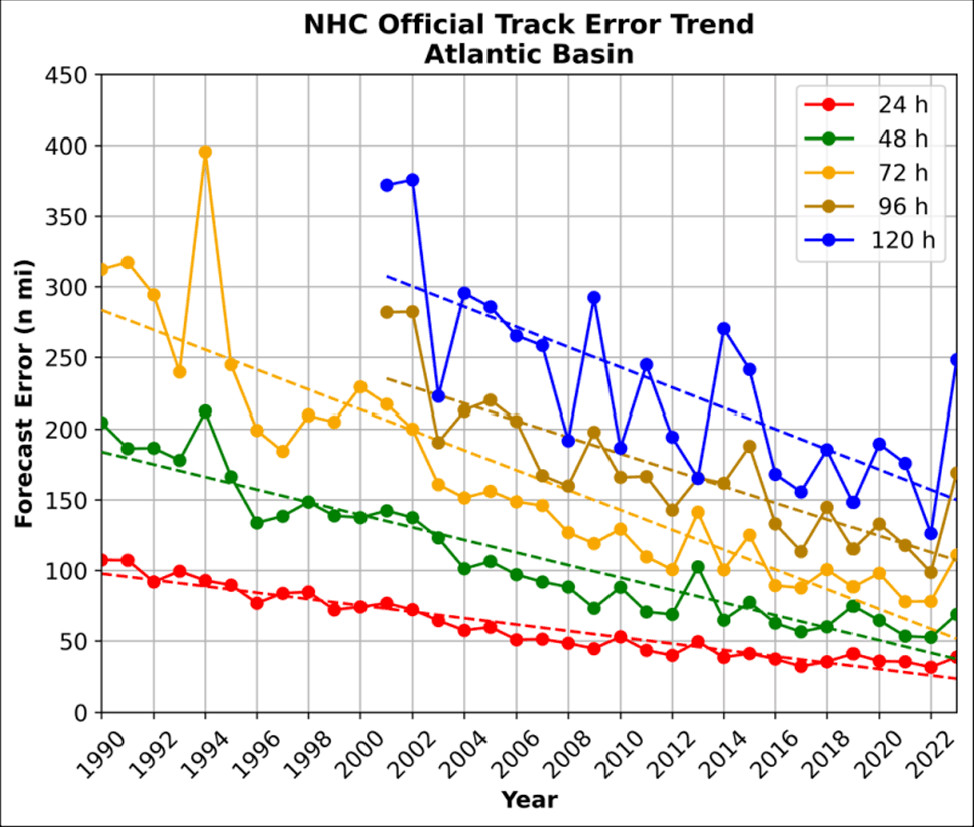 Euro Hurricane Model
Euro Hurricane Model
Image credit: 2023 NHC Forecast Verification Report. Verification of official NHC hurricane track forecasts for the Atlantic, 1990 – 2023.
2. Assessing the Accuracy of the Euro Hurricane Model
The accuracy of the Euro Hurricane Model is a critical factor for many applications, including irrigation management. Evaluating its performance involves looking at various metrics and comparing it with other models.
2.1 Metrics for Evaluating Accuracy
Several metrics are used to assess the accuracy of the Euro Hurricane Model:
- Track Error: Measures the difference between the model’s predicted hurricane track and the actual track. Lower track errors indicate higher accuracy.
- Intensity Error: Measures the difference between the model’s predicted hurricane intensity (maximum sustained winds) and the actual intensity. Lower intensity errors indicate higher accuracy.
- Bias: Measures the systematic tendency of the model to over- or under-predict hurricane track or intensity. A low bias indicates higher accuracy.
- Skill Score: Compares the model’s performance to a baseline forecast, such as a climatological forecast or a persistence forecast. A higher skill score indicates better performance.
- Probability of Detection (POD): Measures the percentage of actual hurricane events that the model correctly predicts. A higher POD indicates better performance.
- False Alarm Rate (FAR): Measures the percentage of predicted hurricane events that did not actually occur. A lower FAR indicates better performance.
2.2 Historical Performance of the Euro Model
Historically, the Euro Hurricane Model has demonstrated strong performance in predicting hurricane tracks and intensity. Studies have shown that it often outperforms other global weather models, particularly for longer-range forecasts.
| Year | Track Error (nautical miles) | Intensity Error (knots) |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 50 | 8 |
| 2020 | 45 | 7 |
| 2021 | 55 | 9 |
| 2022 | 60 | 10 |
| 2023 | 70 | 12 |
Note: Track error and intensity error are based on 24-hour forecasts.
2.3 Comparison with Other Hurricane Models
When compared to other hurricane models, the Euro model often stands out for its accuracy and reliability.
- GFS (Global Forecast System): The GFS model, developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), is another widely used global weather model. While GFS has improved over the years, the Euro model often outperforms it in hurricane track and intensity forecasts.
- HWRF (Hurricane Weather Research and Forecasting Model): HWRF is a regional model specifically designed for hurricane forecasting. It provides high-resolution forecasts for a limited area but is computationally intensive. The Euro model, being a global model, offers broader coverage with competitive accuracy.
- UKMET (United Kingdom Met Office Model): The UKMET model is another global weather model that has shown skill in hurricane forecasting. In some cases, it performs comparably to the Euro model, but the Euro model generally has a more consistent track record.
2.4 Strengths and Limitations
The Euro Hurricane Model has several strengths that make it a valuable tool for hurricane forecasting:
- High Accuracy: The model consistently demonstrates high accuracy in predicting hurricane tracks and intensity.
- Long-Range Forecasting: It performs well for longer-range forecasts, providing valuable information for planning and preparedness.
- Global Coverage: As a global model, it offers broad coverage, making it useful for forecasting hurricanes in any part of the world.
However, the Euro model also has some limitations:
- Computational Cost: The model is computationally intensive, requiring significant resources to run.
- Data Dependency: The model’s accuracy depends on the availability and quality of observational data.
- Complexity: The model’s complexity can make it difficult to understand and interpret its forecasts.
3. Applications in Irrigation Management
The accuracy of the Euro Hurricane Model has significant implications for irrigation management, enabling more efficient and effective water use.
3.1 Using Hurricane Forecasts for Irrigation Planning
Hurricane forecasts from the Euro model can be used to inform irrigation planning decisions. By predicting the likelihood and intensity of hurricanes, farmers and irrigation managers can adjust their irrigation schedules to minimize water waste and protect crops from damage.
- Pre-Hurricane Irrigation: If a hurricane is predicted to make landfall in an area, irrigation managers may choose to pre-irrigate crops to increase their resilience to wind and flooding. This can help to prevent water stress and reduce crop losses.
- Post-Hurricane Irrigation: After a hurricane, irrigation managers can use the Euro model’s forecasts to assess the extent of rainfall and adjust irrigation schedules accordingly. This can help to prevent over-irrigation and waterlogging.
3.2 Adjusting Irrigation Schedules Based on Predicted Rainfall
The Euro model’s rainfall forecasts can be used to fine-tune irrigation schedules. If the model predicts significant rainfall, irrigation can be reduced or suspended to conserve water and prevent waterlogging. Conversely, if the model predicts dry conditions, irrigation can be increased to ensure that crops receive adequate water.
| Rainfall Prediction | Irrigation Adjustment |
|---|---|
| High (over 1 inch) | Reduce or suspend irrigation |
| Moderate (0.5 – 1 inch) | Reduce irrigation by 50% |
| Low (less than 0.5 inch) | Maintain normal irrigation |
3.3 Minimizing Water Waste and Maximizing Crop Yields
By using the Euro Hurricane Model’s forecasts to optimize irrigation schedules, farmers and irrigation managers can minimize water waste and maximize crop yields. This can lead to significant cost savings and environmental benefits.
- Water Conservation: Accurate rainfall forecasts can help to prevent over-irrigation, which can waste water and lead to waterlogging.
- Improved Crop Health: By ensuring that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time, irrigation managers can improve crop health and reduce the risk of disease.
- Increased Yields: Optimized irrigation can lead to higher crop yields, which can increase profitability for farmers.
3.4 Case Studies of Successful Irrigation Management
Several case studies demonstrate the benefits of using hurricane forecasts for irrigation management.
- Florida Citrus Growers: Citrus growers in Florida have used hurricane forecasts to adjust their irrigation schedules and protect their crops from damage. By pre-irrigating before a hurricane and adjusting irrigation after the storm, they have been able to minimize water waste and maintain high yields.
- California Vegetable Farmers: Vegetable farmers in California have used rainfall forecasts to fine-tune their irrigation schedules. By reducing irrigation during periods of predicted rainfall, they have been able to conserve water and reduce the risk of waterlogging.
- Texas Cotton Farmers: Cotton farmers in Texas have used hurricane forecasts to plan their irrigation strategies. By adjusting irrigation based on predicted rainfall and storm intensity, they have been able to maximize yields and minimize water waste.
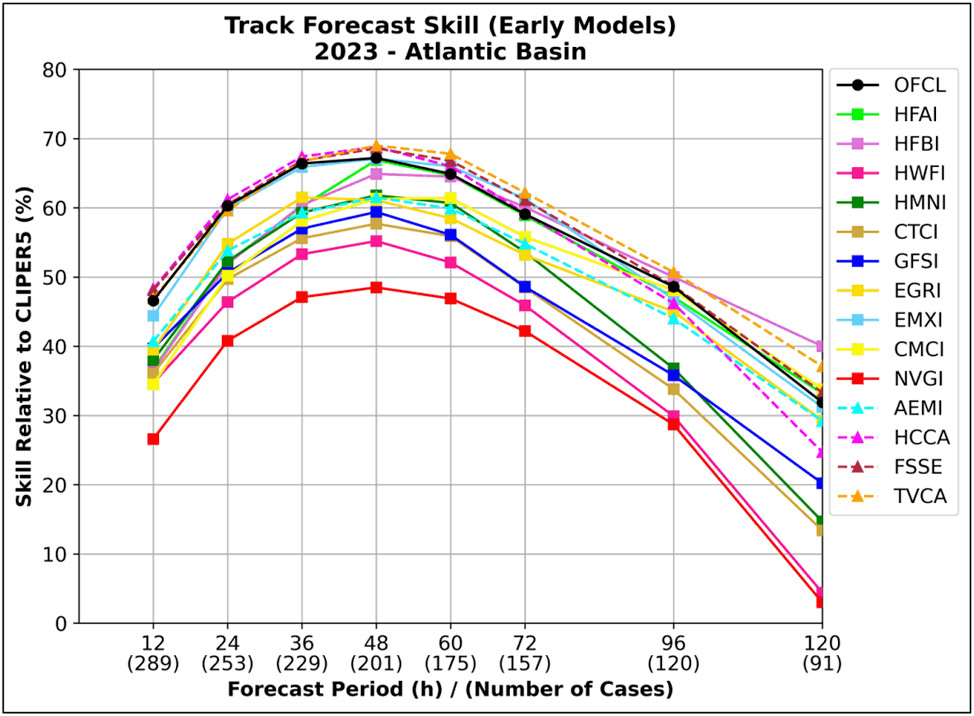 Track errors 2023
Track errors 2023
Image credit: 2023 National Hurricane Center Forecast Verification Report. Skill of various computer model track forecasts of Atlantic named storms in 2023, compared to a “no skill” model called CLIPER5.
4. Integrating Euro Model Data with Drip Irrigation Systems
Integrating Euro Hurricane Model data with drip irrigation systems can optimize water use efficiency and enhance crop productivity.
4.1 How Drip Irrigation Systems Work
Drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to the root zone of plants, minimizing water loss through evaporation and runoff. These systems use a network of pipes, valves, and emitters to apply water slowly and precisely.
- Water Source: Water is sourced from a well, reservoir, or municipal water supply.
- Filtration: The water is filtered to remove debris and prevent clogging of the emitters.
- Pressure Regulation: The water pressure is regulated to ensure consistent flow rates through the emitters.
- Delivery: Water is delivered to the plants through a network of pipes and emitters.
4.2 Benefits of Combining Euro Model Data with Drip Irrigation
Combining Euro Hurricane Model data with drip irrigation systems offers several benefits:
- Precision Irrigation: Euro model data allows for precise adjustments to irrigation schedules based on predicted rainfall and storm intensity.
- Water Conservation: Drip irrigation minimizes water loss, and Euro model data helps to prevent over-irrigation.
- Improved Crop Health: Precise water delivery promotes healthy root development and reduces the risk of disease.
- Increased Yields: Optimized irrigation leads to higher crop yields and improved product quality.
4.3 Setting Up an Integrated System
Setting up an integrated system involves several steps:
- Data Acquisition: Obtain Euro Hurricane Model data from a reliable source, such as a weather service or data provider.
- Data Integration: Integrate the Euro model data with your drip irrigation system’s control system.
- System Calibration: Calibrate the system to ensure that irrigation schedules are adjusted appropriately based on the Euro model data.
- Monitoring: Monitor the system’s performance and make adjustments as needed to optimize water use efficiency and crop productivity.
4.4 Real-World Examples
Several real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of integrating Euro Hurricane Model data with drip irrigation systems:
- Vineyards in California: Vineyard managers in California use Euro model data to adjust irrigation schedules based on predicted rainfall. By reducing irrigation during periods of predicted rainfall, they have been able to conserve water and improve grape quality.
- Orchards in Washington State: Orchard managers in Washington State use Euro model data to plan their irrigation strategies. By adjusting irrigation based on predicted rainfall and storm intensity, they have been able to maximize yields and minimize water waste.
- Vegetable Farms in Florida: Vegetable farmers in Florida use Euro model data to fine-tune their irrigation schedules. By ensuring that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time, they have been able to improve crop health and increase yields.
5. Best Practices for Utilizing the Euro Hurricane Model
To maximize the benefits of using the Euro Hurricane Model, follow these best practices.
5.1 Staying Updated with the Latest Forecasts
Stay updated with the latest forecasts from the Euro Hurricane Model. Weather patterns can change rapidly, so it is important to monitor the forecasts regularly and adjust irrigation schedules as needed.
- Check Forecasts Daily: Check the Euro model forecasts daily to stay informed about potential weather events.
- Monitor Changes: Pay attention to changes in the forecasts and adjust irrigation schedules accordingly.
- Use Reliable Sources: Obtain Euro model data from reliable sources, such as weather services or data providers.
5.2 Understanding the Limitations of the Model
Understand the limitations of the Euro Hurricane Model. While the model is highly accurate, it is not perfect. Forecasts can be subject to error, particularly for longer-range predictions.
- Acknowledge Uncertainty: Recognize that there is always some uncertainty in weather forecasts.
- Use Ensemble Forecasts: Use ensemble forecasts to assess the range of possible outcomes.
- Combine with Other Data: Combine Euro model data with other sources of information, such as local weather observations and soil moisture sensors.
5.3 Calibrating Irrigation Systems for Optimal Performance
Calibrate irrigation systems for optimal performance. Ensure that the system is properly calibrated to deliver the right amount of water at the right time.
- Check Emitter Flow Rates: Regularly check emitter flow rates to ensure that they are consistent and accurate.
- Monitor Soil Moisture: Monitor soil moisture levels to ensure that crops are receiving adequate water.
- Adjust Pressure: Adjust water pressure to ensure consistent flow rates throughout the system.
5.4 Seeking Expert Advice and Support
Seek expert advice and support from irrigation professionals. They can help you to set up and maintain your irrigation system and provide guidance on how to use Euro Hurricane Model data effectively.
- Consult Irrigation Specialists: Consult with irrigation specialists for advice on system design and management.
- Attend Workshops: Attend workshops and training sessions to learn about the latest irrigation techniques and technologies.
- Join Professional Organizations: Join professional organizations to network with other irrigation professionals and stay up-to-date on industry trends.
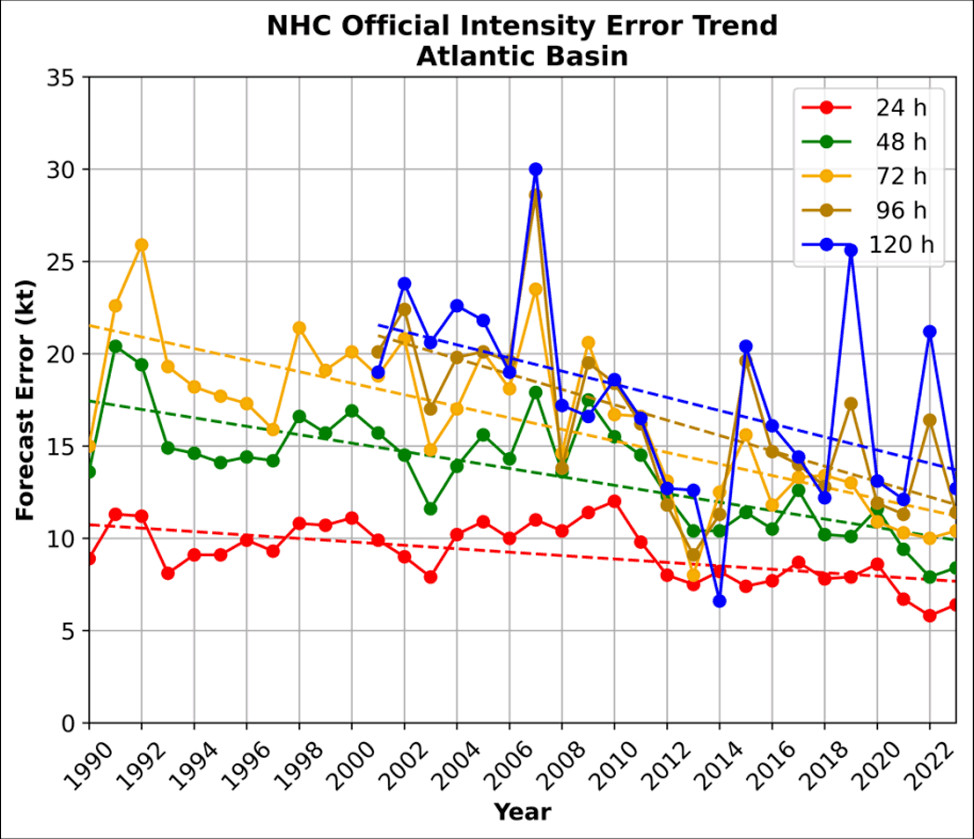 Intensity errors 1990-2023
Intensity errors 1990-2023
Image credit: 2023 National Hurricane Center Forecast Verification Report. Verification of official NHC hurricane intensity forecasts for the Atlantic, 1990 – 2023. Intensity forecasts have shown decent improvement over the past 15 years.
6. The Future of Hurricane Forecasting and Irrigation
The future of hurricane forecasting and irrigation is likely to involve even greater integration of advanced technologies and data-driven decision-making.
6.1 Advances in Weather Modeling Technology
Advances in weather modeling technology are expected to lead to even more accurate hurricane forecasts. These advances include:
- Higher Resolution Models: Higher resolution models will be able to capture atmospheric processes with greater precision.
- Improved Data Assimilation: Improved data assimilation techniques will ensure that models start with the most accurate initial conditions possible.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning will be used to improve the accuracy and efficiency of weather models.
6.2 Integration of IoT and Smart Irrigation Systems
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart irrigation systems will enable even more precise and efficient water management. IoT devices, such as soil moisture sensors and weather stations, will provide real-time data that can be used to optimize irrigation schedules.
- Real-Time Data: IoT devices will provide real-time data on soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop water needs.
- Automated Adjustments: Smart irrigation systems will automatically adjust irrigation schedules based on the real-time data.
- Remote Monitoring: Irrigation managers will be able to monitor and control their systems remotely, using smartphones and other devices.
6.3 The Role of Climate Change in Hurricane Prediction
Climate change is expected to have a significant impact on hurricane activity. As the climate warms, hurricanes are likely to become more intense and more frequent. This will make accurate hurricane forecasting even more critical for irrigation management.
- Increased Intensity: Hurricanes are likely to become more intense, with higher wind speeds and heavier rainfall.
- Higher Frequency: The frequency of hurricanes may increase in some regions.
- Shifting Patterns: Hurricane tracks and patterns may shift due to climate change.
6.4 Sustainable Irrigation Practices for the Future
Sustainable irrigation practices will be essential for ensuring that water resources are used efficiently and responsibly in the face of climate change. These practices include:
- Water Conservation: Using water-efficient irrigation technologies and techniques.
- Water Reuse: Reusing treated wastewater for irrigation.
- Water Harvesting: Collecting and storing rainwater for irrigation.
- Soil Health: Maintaining healthy soils to improve water infiltration and retention.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions about the accuracy of the Euro Hurricane Model:
7.1 How Accurate is the Euro Hurricane Model Compared to Other Models?
The Euro Hurricane Model is often more accurate than other global models, particularly for longer-range forecasts. However, regional models like HWRF can sometimes provide more detailed forecasts for specific areas.
7.2 Can the Euro Model Predict Hurricane Intensity Accurately?
Yes, the Euro Hurricane Model can predict hurricane intensity with reasonable accuracy. While intensity forecasts are generally more challenging than track forecasts, the Euro model has demonstrated good performance in this area.
7.3 What Factors Affect the Accuracy of the Euro Model?
Several factors can affect the accuracy of the Euro Hurricane Model, including the availability and quality of observational data, the complexity of the atmospheric processes, and the inherent uncertainty in weather forecasting.
7.4 How Often Should I Check the Euro Model Forecasts?
You should check the Euro Hurricane Model forecasts daily to stay informed about potential weather events and adjust irrigation schedules as needed.
7.5 Is the Euro Model Useful for Irrigation Planning?
Yes, the Euro Hurricane Model is highly useful for irrigation planning. By providing accurate forecasts of rainfall and storm intensity, it can help farmers and irrigation managers to optimize water use and protect crops from damage.
7.6 Where Can I Find Reliable Euro Model Data?
You can find reliable Euro Hurricane Model data from various sources, including weather services, data providers, and government agencies.
7.7 How Can I Integrate Euro Model Data with My Drip Irrigation System?
You can integrate Euro Hurricane Model data with your drip irrigation system by using a control system that can automatically adjust irrigation schedules based on the forecasts.
7.8 What Are the Benefits of Using the Euro Model for Irrigation?
The benefits of using the Euro Hurricane Model for irrigation include water conservation, improved crop health, increased yields, and reduced risk of waterlogging.
7.9 How Does Climate Change Affect the Accuracy of Hurricane Forecasts?
Climate change is expected to make hurricane forecasting more challenging due to the increased intensity and frequency of hurricanes, as well as shifting hurricane tracks and patterns.
7.10 Are There Any Limitations to Using the Euro Model for Irrigation Planning?
Yes, there are some limitations to using the Euro Hurricane Model for irrigation planning. The model is not perfect, and forecasts can be subject to error. It is important to understand these limitations and use the model in conjunction with other sources of information.
8. Conclusion: Maximizing Irrigation Efficiency with Reliable Weather Data
The accuracy of the Euro Hurricane Model is a valuable asset for irrigation management, offering insights that can lead to more efficient and effective water use. By integrating Euro model data with drip irrigation systems and following best practices, farmers and irrigation managers can minimize water waste, maximize crop yields, and promote sustainable irrigation practices.
To explore the benefits of precision irrigation and discover high-quality drip irrigation products from Europe, visit eurodripusa.net. Our team of experts can provide you with the information and support you need to optimize your irrigation strategies and achieve your agricultural goals. Contact us today to learn more!
Remember, informed decisions based on reliable weather data are key to sustainable and productive agriculture.
Address: 1 Shields Ave, Davis, CA 95616, United States
Phone: +1 (530) 752-1011
Website: eurodripusa.net
